Abstract
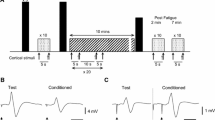
During fatiguing exercise corticomotor excitability increases as force declines, which may serve to increase motor output to the exercising muscle, but paradoxically at the same time there is an increase in silent period (SP) duration which is thought to represent a build-up of intracortical inhibition. Paired-pulse TMS at long interstimulus intervals can also be used to derive an index of long-interval cortical inhibition (LICI), however this has not yet been investigated in fatigue. Our aim was to measure LICI during and after a fatiguing exercise and determine if the changes in the index of LICI parallel the changes in SP duration. To do this, we used single and paired-pulse TMS to measure motor evoked potential (MEP) amplitude, LICI and SP duration during, and for 10 min after, a 10-min intermittent maximal fatiguing exercise of the index finger, designed to fatigue the first dorsal interosseous (FDI) muscle (force after 10-min of exercise 64 ± 7% of baseline, P < 0.05). Single-pulse MEP amplitude and SP duration were increased during fatiguing exercise (minute 10; 179 ± 24% and 128 ± 9% of baseline, respectively, P < 0.05), in contrast the measure of LICI was reduced compared to baseline (minute 10; 0.45 ± 0.17 vs. baseline; 0.70 ± 0.10, P < 0.05). These results suggest that SP duration and LICI may reflect processes occurring in different neuronal populations. The increased SP duration may correspond to processes of central fatigue in centres ‘upstream’ of primary motor cortex (M1), whereas the decrease in LICI, together with increased MEP amplitude, are consistent with an increase in M1 output during fatigue that may serve to compensate for reduced central drive.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benwell NM, Sacco P, Hammond GR, Byrnes ML, Mastaglia FL, Thickbroom GW (2006) Short-interval cortical inhibition and corticomotor excitability with fatiguing hand exercise: a central adaptation to fatigue? Exp Brain Res 170:191–198
Brasil-Neto JP, Pascual-Leone A, Valls-Sole J, Cammarota A, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1993) Postexercise depression of motor evoked potentials: a measure of central nervous system fatigue. Exp Brain Res 93:181–184
Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Valls-Sole J, Pascual-Leone A, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1995) Role of intracortical mechanisms in the late part of the silent period to transcranial stimulation of the human motor cortex. Acta Neurol Scand 92:383–386
Chen R (2004) Interactions between inhibitory and excitatory circuits in the human motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 154:1–10
Chen R, Lozano AM, Ashby p (1999) Mechanism of the silent period following transcranial magnetic stimulation. Evidence from epidural recordings. Exp Brain Res 128:539–542
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Meglio M, Cioni B, Tamburrini G, Tonali P, Rothwell JC (2000) Direct demonstration of the effect of lorazepam on the excitability of the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 111:794–799
Gandevia SC, Allen GM, Butler JE, Taylor JL (1996) Supraspinal factors in human muscle fatigue: evidence for suboptimal output from the motor cortex. J Physiol 490:529–536
Hanajima R, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Sakai K, Furubayashi T, Machii K, Kanazawa I (1998) Paired-pulse magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex: differences among I waves. J Physiol 509(Pt 2):607–618
Inghilleri M, Berardelli A, Cruccu G, Manfredi M (1993) Silent period evoked by transcranial stimulation of the human cortex and cervicomedullary junction. J Physiol 466:521–534
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Liepert J, Kotterba S, Tegenthoff M, Malin JP (1996) Central fatigue assessed by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Muscle Nerve 19:1429–1434
McDonnell MN, Orekhov Y, Ziemann U (2006) The role of GABA(B) receptors in intracortical inhibition in the human motor cortex. Exp Brain Res (DOI: 10.1007/s00221-006-0365-2)
Pierantozzi M, Grazia Marciani M, Giuseppina Palmieri M, Brusa L, Galati S, Donatella Caramia M, Bernardi G, Stanzione P (2004) Effect of Vigabatrin on motor responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation: an effective tool to investigate in vivo GABAergic cortical inhibition in humans. Brain Res 1028:1–8
Roick H, Vongiesen HJ, Benecke R (1993) On the origin of the postexcitatory inhibition seen after transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in awake human subjects. Exp Brain Res 94:489–498
Rossini PM, Barker AT, Berardelli A, Caramia MD, Caruso G, Cracco RQ, Dimitrijevic MR, Hallett M, Katayama Y, Lucking CH, et al (1994) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical application. Report of an IFCN committee. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 91:79–92
Sacco P, Thickbroom GW, Thompson ML, Mastaglia FL (1997) Changes in corticomotor excitation and inhibition during prolonged sub-maximal muscle contractions. Muscle Nerve 20:1158–1166
Sacco P, Thickbroom GW, Byrnes ML, Mastaglia FL (2000) Changes in corticomotor excitability after fatiguing muscle contractions. Muscle Nerve 23:1840–1846
Samii A, Wassermann EM, Ikoma K, Mercuri B, Hallett M (1996) Characterization of postexercise facilitation and depression of motor evoked potentials to transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 46:1376–1382
Samii A, Canos M, Ikoma K, Wassermann EM, Hallett M (1997) Absence of facilitation or depression of motor evoked potentials after contralateral homologous muscle activation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 105:241–245
Sanger TD, Garg RR, Chen R (2001) Interactions between two different inhibitory systems in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 530:307–317
Taylor JL, Butler JE, Allen GM, Gandevia SC (1996) Changes in motor cortical excitability during human muscle fatigue. J Physiol 490:519–528
Taylor JL, Allen GM, Butler JE, Gandevia SC (2000) Supraspinal fatigue during intermittent maximal voluntary contractions of the human elbow flexors. J Appl Physiol 89:305–313
Tergau F, Wanschura V, Canelo M, Wischer S, Wassermann EM, Ziemann U, Paulus W (1999) Complete suppression of voluntary motor drive during the silent period after transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 124:447–454
Valls-Sole J, Pascual-Leone A, Wassermann EM, Hallett M (1992) Human motor evoked responses to paired transcranial magnetic stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:355–364
Wassermann EM, Samii A, Mercuri B, Ikoma K, Oddo D, Grill SE, Hallett M (1996) Responses to paired transcranial magnetic stimuli in resting, active, and recently activated muscles. Exp Brain Res 109:158–163
Werhahn KJ, Kunesch E, Noachtar S, Benecke R, Classen J (1999) Differential effects on motorcortical inhibition induced by blockade of GABA uptake in humans. J Physiol 517:591–597
Wilson SA, Thickbroom GW, Mastaglia FL (1993) Transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping of the motor cortex in normal subjects. The representation of two intrinsic hand muscles. J Neurol Sci 118:134–144
Wu T, Sommer M, Tergau F, Paulus W (2000) Modification of the silent period by double transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1868–1872
Zanette G, Bonato C, Polo A, Tinazzi M, Manganotti P, Fiaschi A (1995) Long-lasting depression of motor-evoked potentials to transcranial magnetic stimulation following exercise. Exp Brain Res 107:80–86
Ziemann U, Netz J, Szelenyi A, Homberg V (1993) Spinal and supraspinal mechanisms contribute to the silent period in the contracting soleus muscle after transcranial magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Neurosci Lett 156:167–171
Ziemann U, Lonnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W (1996a) Effects of antiepileptic drugs on motor cortex excitability in humans: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Ann Neurol 40:367–378
Ziemann U, Lonnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W (1996b) The effect of lorazepam on the motor cortical excitability in man. Exp Brain Res 109:127–135
Ziemann U, Chen R, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1998) Dextromethorphan decreases the excitability of the human motor cortex. Neurology 51:1320–1324
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Neuromuscular Foundation of Western Australia. NMB is a recipient of an Australian Postgraduate Award, a Jean Rogerson Postgraduate Scholarship and a Woodside Neurotrauma Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benwell, N.M., Mastaglia, F.L. & Thickbroom, G.W. Differential changes in long-interval intracortical inhibition and silent period duration during fatiguing hand exercise. Exp Brain Res 179, 255–262 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0790-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0790-2