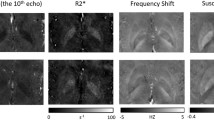
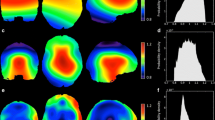
The ability to analyze and merge data across sites, vendors, and field strengths depends on one's ability to acquire images with the same image quality including image smoothness, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). SNR can be used to compare different magnetic resonance scanners as a measure of comparability between the systems. This study looks at the SNR and CNR ratios in structural fast spin-echo T2-weighted scans acquired in five individuals across ten sites that are part of Functional Imaging Research of Schizophrenia Testbed Biomedical Informatics Research Network (fBIRN). Different manufacturers, field strengths, gradient coils, and RF coils were used at these sites. The SNR of gray matter was fairly uniform (41.3–43.3) across scanners at 1.5 T. The higher field scanners produced images with significantly higher SNR values (44.5–108.7 at 3 T and 50.8 at 4 T). Similar results were obtained for CNR measurements between gray/white matter at 1.5 T (9.5–10.2), again increasing at higher fields (10.1–28.9 at 3 T and 10.9 at 4 T).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Gurleyik E Haacke (2002) ArticleTitleQuantification of errors in volume measurements of the caudate nucleus using magnetic resonance imaging J Magn Reson Imaging 15 353–363 Occurrence Handle11948824 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jmri.10083
Zou K, Greve D, Wang M, Pieper S, Warfield S, White N, Vangel M, Kikinis R, Wells W, BIRN F: A prospective multi-institute study of the reproducibility of fMRI: A preliminary report from the biomedical informatics research group. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. 2, 2004, pp 769–776
K Zou DN Greve M Wang S Pieper S Warfield NS White S Manandhar CG Brown MG Vangel R Kikinis WM Wells InstitutionalAuthorNameBIRN F (2005) ArticleTitleFactors impacting the reproducibility of functional MR Imaging: Preliminary results of a prospective multiinstitutional study by the biomedical informatics research network Radiology 237 781–789 Occurrence Handle16304101
Friedman L, Magnotta V, Posse S, BIRN F: Scanner differences in the smoothness of fMRI images: Implications for multi-center studies, In: International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2004, p 1074
N Andreasen G Cohen G Harris T Cizadlo (1992) ArticleTitleImage processing for the study of brain structure and function: Problems and programs J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 4 125–133 Occurrence Handle1627972 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A3s%2FkvFY%3D
N Andreasen T Cizadlo G Harris T Cizadlo (1993) ArticleTitleVoxel processing techniques for the antemortem study of neuroanatomy and neuropathology using magnetic resonance imaging J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 5 121–130 Occurrence Handle8508032 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB1czptlA%3D
V Magnotta G Harris N Andreasen W Yuh D Heckel (2002) ArticleTitleStructural MR image processing using the BRAINS2 toolbox Comput Med Imaging Graph 26 251–264 Occurrence Handle12074920 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0895-6111(02)00011-3
Ibanez L, Schroeder W, Ng L, Cates J: The ITK Software Guide: The Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit (version 1.4), Kitware Inc, Clifton Park, NY, 2003
P Viola W Wells (1995) Alignment by maximization of mutual information International Conference on Computer Vision IEEE Computer Society Press Los Alamitos, CA 16–23
F Maes A Collignon D Vandermeulen G Marchal P Suetens (1997) ArticleTitleMulti-modality image registration by maximization of mutual information IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16 187–198 Occurrence Handle9101328 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB2MrpvFM%3D Occurrence Handle10.1109/42.563664
P Bottomley C Hardy R Argersinger L Pfeifer (1998) ArticleTitleA review of normal tissue hydrogen NMR relaxation times and relaxation mechanisms from 1–100 MHz: dependence on tissue type, NMR frequency, temperature, species, excision, and age Med Phys 11 425–448 Occurrence Handle10.1118/1.595535
P Jezzard S Duewell R Balaban (1996) ArticleTitleMR relaxation times in human brain: Measurements at 4 T Radiology 199 773–779 Occurrence Handle8638004 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB38%2FlsVY%3D
N Gelman J Gorell P Baker R Savage E Spickler J Windham R Knight (1999) ArticleTitleMR imaging of human brain at 3.0t: Preliminary report on transverse relation rates and relation to estimated iron content Radiology 210 759–767 Occurrence Handle10207479 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3itlyrtA%3D%3D
C Georgiades R Itoh X Golay P Zijl Particlevan E Melhem (1999) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the human brain at 1.5 T: Regional variations in transverse relation rates in the cerebral cortex Radiology 210 759–767
J Vymazaland M Babis RA Brooks K Filip M Dezortova M Hajek (1996) ArticleTitleT1 and T2 alterations in the brains of patients with hepatic cirrhosis AJNR 17 333–336
J Wansapura S Holland R Dunn W Ball (1999) ArticleTitleNMR relaxation times in the human brain at 3.0 tesla J Magn Reson Imaging 9 531–538 Occurrence Handle10232510 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3kslCksg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-2586(199904)9:4<531::AID-JMRI4>3.0.CO;2-L
K Whittal A MacKay A Graeb R Nugent K Li W Paty (1997) ArticleTitleIn vivo measurement of T2 distributions and water contents in normal human brain Magn Reson Med 37 34–43
FD Doty G Entzminger C Hauck JP Staab (1999) ArticleTitlePractical aspects of birdcage coils J Magn Reson 138 144–154 Occurrence Handle10329237 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivVKhtLY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmre.1998.1703
Tropp JS: Method of correcting an asymmetry in an NMR radio frequency coil and an improved radio frequency coil having N-fold symmetry and reduced eddy current, US Patent No 5,196,797, 1993
Wardenier P: Local intensity shift artifact (LISA). In: Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 1989, 1998, pp 1175
RW Jones RF Witte (2000) ArticleTitleSignal intensity artifacts in clinical MR imaging Radiographics 20 893–901 Occurrence Handle10835135 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3psFaqsQ%3D%3D
Vij K, Jones R, Boskamp E: The asymmetric birdcage design: a quadrature neck coil application. In: Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 1992, 1992, p 1040
Acknowledgments
This work was collected as part of the Functional Imaging Research of Schizophrenia Testbed (FIRST), Biomedical Informatics Research Network (BIRN). The authors would like to thank all of the people who have worked so hard to make the fBIRN project successful and who helped to collect this data. This work was supported in part by the following NIH NCRR Grant: NCRR P41RR13218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnotta, V.A., Friedman, L. & FIRST BIRN. Measurement of Signal-to-Noise and Contrast-to-Noise in the fBIRN Multicenter Imaging Study. J Digit Imaging 19, 140–147 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-006-0264-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-006-0264-x