Abstract
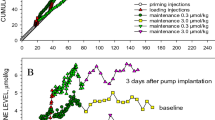
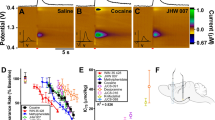
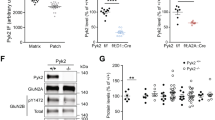
LONG term effects of the amphetamine drugs on enzymes relevant to neurotransmitter biosynthesis and catabolism have created considerable interest. Utena et al.1 have shown that chronic amphetamine administration leads to a biphasic change in monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity during administration, and produces a prolonged increase in MAO activity which outlasts the presence of the drug. Javoy et al.2, using intraventricularly administered isotopic norepinephrine, have shown that a marked increase in turnover of norepinephrine follows amphetamine administration. This could indicate that the activity of the rate limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of norepinephrine, tyrosine hydroxylase, was increased. This kind of change has been attributed to the loss of a tonic allosteric product inhibition by norepinephrine and is thought to result from the depletion of intracellular norepinephrine by the actions of amphetamine in releasing and blocking re-uptake of synaptic norepinephrine3. Another potential mechanism for this kind of alteration, and one which would be likely to outlast both the presence of the drug or the norepinephrine depleted state, would be a change in the level of the rate limiting enzyme. In a preliminary communication, we reported some evidence suggesting that methedrine (+N-methylamphetamine) might increase the specific activity of brain tyrosine hydroxylase and that this mechanism was cycloheximide sensitive4. We document here this kind of amphetamine induced change in tyrosine hydroxylase in the adrenal medulla and, in addition, confirm a similar effect with reserpine and 6-hydroxydopamine which has already been reported by Mueller et al.5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Utena, H., Ezoe, T., Kato, N., and Hada, H., J. Neurochem., 4, 161 (1959).
Javoy, F., Thierry, A. M., Kety, S. S., and Glowinski, J., Comm. Behav. Biol., 1, 43 (1968).
Udenfriend, S., in Ciba Foundation Study Group on Adrenergic Neurotransmission, 33, 3 (Little, Brown, 1968).
Mandell, A. J., Morgan, M., and Oliver, G. W., in N.I.M.H. Study Group Report on the Biology of Depression (edit. by Katz, M., and Williams, T.) (US Government Printing Office, 1970, in the press).
Mueller, R. A., Thoeneu, H., and Axelrod, J., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 169, 74 (1969).
Levitt, M., Gibb, J. W., Daly, J. W., Lipton, M., and Udenfriend, S., Biochem. Pharmacol., 16, 1313 (1967).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265 (1951).
Schrier, B. K., and Shuster, L., J. Neurochem., 14, 977 (1967).
Mueller, R. A., Thoeneu, H., and Axelrod, J., Mol. Pharmacol., 5, 463 (1969).
Mueller, R. A., Thoeneu, H., and Axelrod, J., Science, 163, 468 (1969).
Weiner, N., and Rabadjija, M., J. Pharm. Exp. Therap., 164, 103 (1968).
Mandell, A. J., and Spooner, C. E., Science, 162, 1442 (1968).
Mandell, A. J., Spooner, C. E., Winters, W. D., Cruikshank, M., and Sabbot, J. M., Intern. J. Neuropharm., 8, 235 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MANDELL, A., MORGAN, M. Amphetamine Induced Increase in Tyrosine Hydroxylase Activity. Nature 227, 75–76 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/227075a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/227075a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.